What is dialysis?
When the kidney lose their function, excess biochemical material, excess fluids and unwanted waste from the blood is filtered outusing a lifesaving medical procedure called Dialysis.
Who needs dialysis?
- For the patients with glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of less than 15, categorised under Stage-5 or End Stage Renal failure who has become symptomatic.
- For the patients who are suffering from total kidney failure qualify for dialysis
Is there any alternative treatment for ESRD other than dialysis?
- The only alternative treatment for ESRD is kidney transplantation
What are the treatment options available for GFR of 30 or below?
- Medication – ACE inhibitors and ARB Blockers
- Advise on Dialysis options and Transplantation
What is the purpose of Dialysis?
- Act as substitute for kidney function
- Removal of waste and extra fluid from the body to prevent them from building and cause complications
- Help in regulating blood pressure
What are the major types of Dialysis?
- Haemodialysis – Blood is purified in an external machine and returned to the body
- Peritoneal Dialysis – Blood is purified within the peritoneal cavity in exchange for dialysis fluid
What are the various dialysis options available?
Haemodialysis through Arteriovenous Fistula (AVF)
- The most common type of dialysis
- Treatment duration is typically 3-5 hours a day and 3 times a week frequency
- Dialysis machine is used to remove waste and extra fluid
- The connections made surgically help to start dialysis in 2 to 3months
- The access for long term dialysis is AV Fistula.
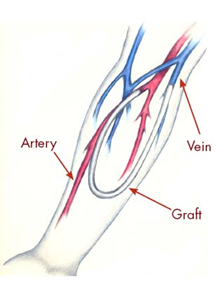
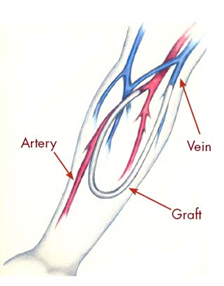
Haemodialysis through Arteriovenous Graft (AVG)
- One of the most common type of dialysis
- Treatment duration is typically 3-5 hours a day and 3 times a week frequency
- Dialysis machine is used to remove waste and extra fluid
- The connections made surgically help to start dialysis in 2 to 3weeks
- The entry port (AVF) is suitable long term dialysis.
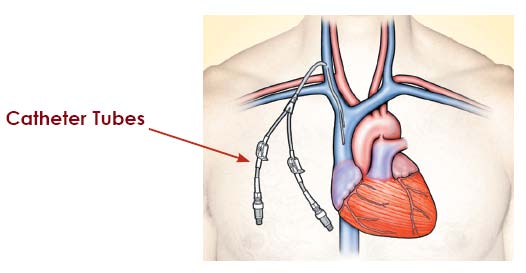
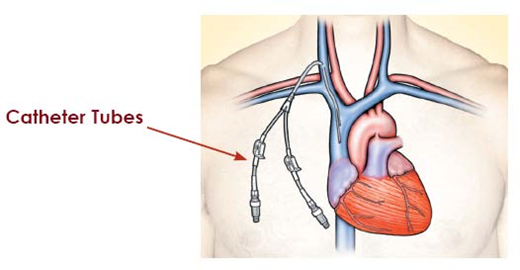
Haemodialysis through Vascular Access Catheter (VAC)
- Mode of dialysis before surgically creating AVF or AVG
- Treatment duration is typically 3-5 hours a day and 3 times a week frequency
- Also helps patients whose blood vessels are weak to support either fistula or graft
- Dialysis machine is used to remove waste and extra fluid
- Non-cuffed tunnelled catheters are used for emergencies and for less than 3weeks
- Tunnelled catheter are used for emergencies and for longer than 3weeks.
Home haemodialysis
- Home dialysis is considered to be more effective than in-centre (Hospital) dialysis
- Home dialysis has been shown to provide clinical improvements in blood pressure regulation, regression of left ventricular hypertrophy, restoration of left ventricular ejection fraction, normalization of phosphate control
- Home dialysis mimics natural kidney function with higher frequency (daily) and shorter dialysis periods (1½ to 2hrs)
- Helps to avoid stressful hospital visits while enabling more time spent at home with family, friends and work
- Helps in better understanding on the condition, treatment process and progress
- Improves health and quality of life when adhered to regular and good practices
Peritoneal Dialysis
- Provides flexibility for dialysis away from hospital i.e. at work, home, while sleeping
- The dialysis catheter is introduced surgically into the abdomen area (peritoneal cavity)
- The blood is purified inside the body using dialysis fluid while being exchanged for waste and excess fluid
- Peritoneal Dialysis should be done 4 to 5 times a day, lasting for 30 to 40mins
- Studies show that the patients who opt peritoneal dialysis live longer than haemodialysis
- mimics natural kidney function with higher frequency (5 times a day) and shorter dialysis periods (30 to 40mins)
- Can be chosen as the preferred dialysis option before haemodialysis and kidney transplantation
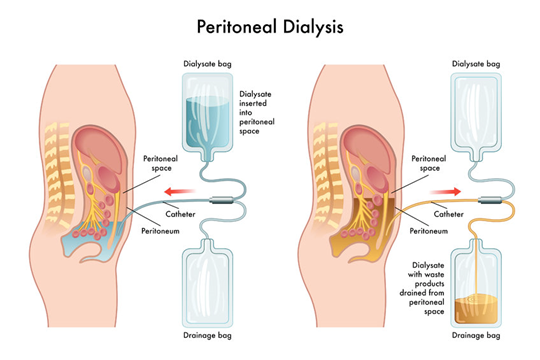
Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD)
- The most portable type of dialysis and doesn’t need needles
- It is done every day, via your peritoneal cavity
- Dialysis fluid is constantly present in the abdomen
- The fluid is typically exchanged four to five times per day
- It requires peritoneal fluid bag changes four to five times a day
- Cleans up the blood as expected
- Helps to maintain the fluid balance
- Effectively replaces the work of the diseased kidneys
Continuous Cyclic Peritoneal Dialysis (CCPD) / Automated Peritoneal Dialysis (APD)
- Patients who qualify as high transporter can opt for APD
- A cycler machine automatically exchanges fluid into and out of the abdomen
- The patient need to spend between 8 and 10 hours a night for CCPD
- Controlled fluid exchange through peritoneal route
- Provides continuous therapy at night without any on/off procedures during the day
- Ideal for at home dialysis for kids, elderly and bedridden
- Cleans up the blood as expected
- Helps to maintain the fluid balance
- Effectively replaces the work of the diseased kidneys
Hemofiltration (CHF)
- Typically used for critically ill patients suffering from Acute Kidney Injury or Sepsis or Organ Failure
- This gradual and continuous therapy also helps hemodynamically unstable patients
- Provides best control of fluid balance
- It takes the advantage over haemodialysis by offering removal of large volumes of fluid continuously while not causing any hypotension episodes
- It also helps in clearance of medium to larger molecules
Hemodiafiltration (HDF)
- Hemofiltration (Continuous)in combination with Haemodialysis (intermittent) is – Hemodiafiltration
- It helps in clearance of small to larger molecules
- It provides potential benefits in overcoming anaemia, inflammation, oxidative stress, dyslipidaemia, and calcium-phosphate imbalances
- HDF is found to be beneficial in both adults and children
What are the self-management tips or recommendations during Dialysis?
- Ensure to get the dialysis done as per the recommended schedule without missing
- Keep the access port clean and dry with necessary infection control measures
- Consult a registered nutritionist and plan diet according to the dialysis option chosen
- Take medication as advised for – heart and blood vessel problems, high blood pressure, anaemia, bone problems, poor nutrition and diabetes
- Exercise regularly for at least 30mins in a day and stay physically active
- Quit smoking and drinking alcohol
- Limit you salt intake to minimum
- Follow strategies to minimise fluid intake
- Maintain healthy weight and lose extra kilos if needed medically